About Customer

Customer is a global food company with a rich history and a reputation for innovation. The company is best known for its iconic invention, instant noodles, which revolutionized the way people consume and enjoy convenient meals. Customer’s commitment to quality and taste is evident in its diverse range of products, which cater to various culinary preferences and dietary needs. From classic flavors to bold and exotic combinations, Customer continuously strives to deliver exceptional dining experiences to consumers worldwide.
Through strategic partnerships and a strong distribution network, Customer has successfully expanded its reach to numerous countries, earning a loyal customer base while maintaining its core values of excellence and customer satisfaction. Customer consistently explores new frontiers in the food industry, embodying the spirit of innovation that has defined its success. The company’s influence extends beyond instant noodles, as it has ventured into other food categories, including frozen foods, snacks, and beverages.
This diversification has appealed to a broader consumer base and helped Customer maintain its global leadership position.
What is F&B Wastewater?
Food and beverage wastewater is a type of wastewater that is generated during the production, processing, and cleaning activities in the food and beverage industry. This type of wastewater contains various organic and inorganic substances, contaminants, and residues derived from food processing operations, cleaning agents, and other sources within the industry. Food and beverage wastewater can vary in composition depending on the specific processes involved, but it generally contains high levels of organic matter, fats, oils, grease, sugars, proteins, and nutrients.
The food and beverage industry encompasses a wide range of sectors, including food processing, beverage production, dairy processing, breweries, wineries, bakeries, meat processing, fruit and vegetable processing, and more. Each sector generates specific types of wastewater based on its operations. For example, meat processing wastewater may contain blood, fats, and proteins, while dairy processing wastewater may have high levels of lactose and whey. The complex characteristics of food and beverage wastewater thus make it challenging to treat and dispose of safely.
The high organic content and nutrient levels in this wastewater can cause environmental issues if not properly managed. The discharge of untreated or poorly treated food and beverage wastewater can also lead to water pollution, oxygen depletion in water bodies, and the growth of harmful microorganisms.
Therefore, effective wastewater treatment is essential to meet environmental regulations and ensure the protection of water resources.
Review of Current Treatments
The Food and Beverage (F&B) industry is a highly water resource-intensive sector. From being an ingredient in your favourite condiment to being used to facilitate daily equipment cleanings, water is as we know, a very valuable resource. Typically, wastewater effluent from F&B processing plants is associated with the following characteristics:
- High concentration of Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Chemical Oxidation Demand (COD), Biological Oxidation Demand (BOD), Fats, Oils, and Grease (FOG).
- Nutrients consisting of Ammonia, Phosphorus and Nitrogen.
- Pathogenic organisms and traces of pesticides.
These characteristics present conundrums for facilities that harness traditional methods (DAF and biological processes) for wastewater treatment, as they may not be able to effectively contain the high contaminant loads that pose a threat to human life and the environment.
Hydroleap’s Solution
To help resolve the presented drawbacks, Hydroleap sought to reduce its water footprint and lower the environmental impacts from its wastewater discharge and solid sludge generation. We thoroughly studied and experimented with the company’s wastewater and concluded that the absence of anions allowed for sludge production which was far more compact in the EC process, as compared to that in chemical coagulation.
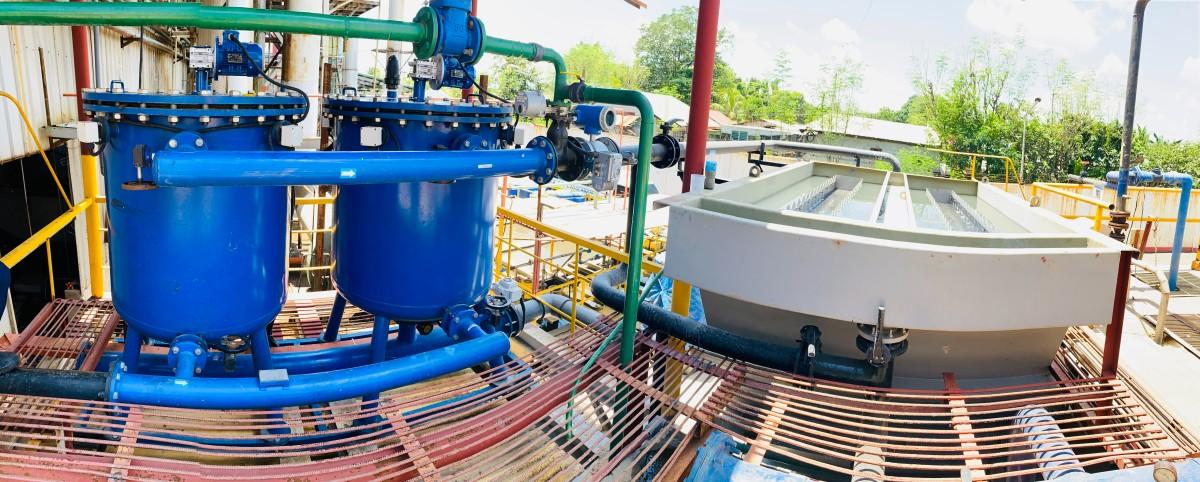
From here, Hydroleap went on to install a 30 m³/hr pre-treatment system along with a lamella clarifier (Figure 1) to replace the existing anaerobic process and clarifier.
Results of Implementation
The Hydroleap system has been successfully implemented at several food and beverage facilities. The results have shown that the system can achieve COD removal rates of up to 68%, BOD removal rates of up to 70%, TSS removal rates of up to 96%, FOG removal rates of up to 95%, and phosphate removal rates of up to 76%.

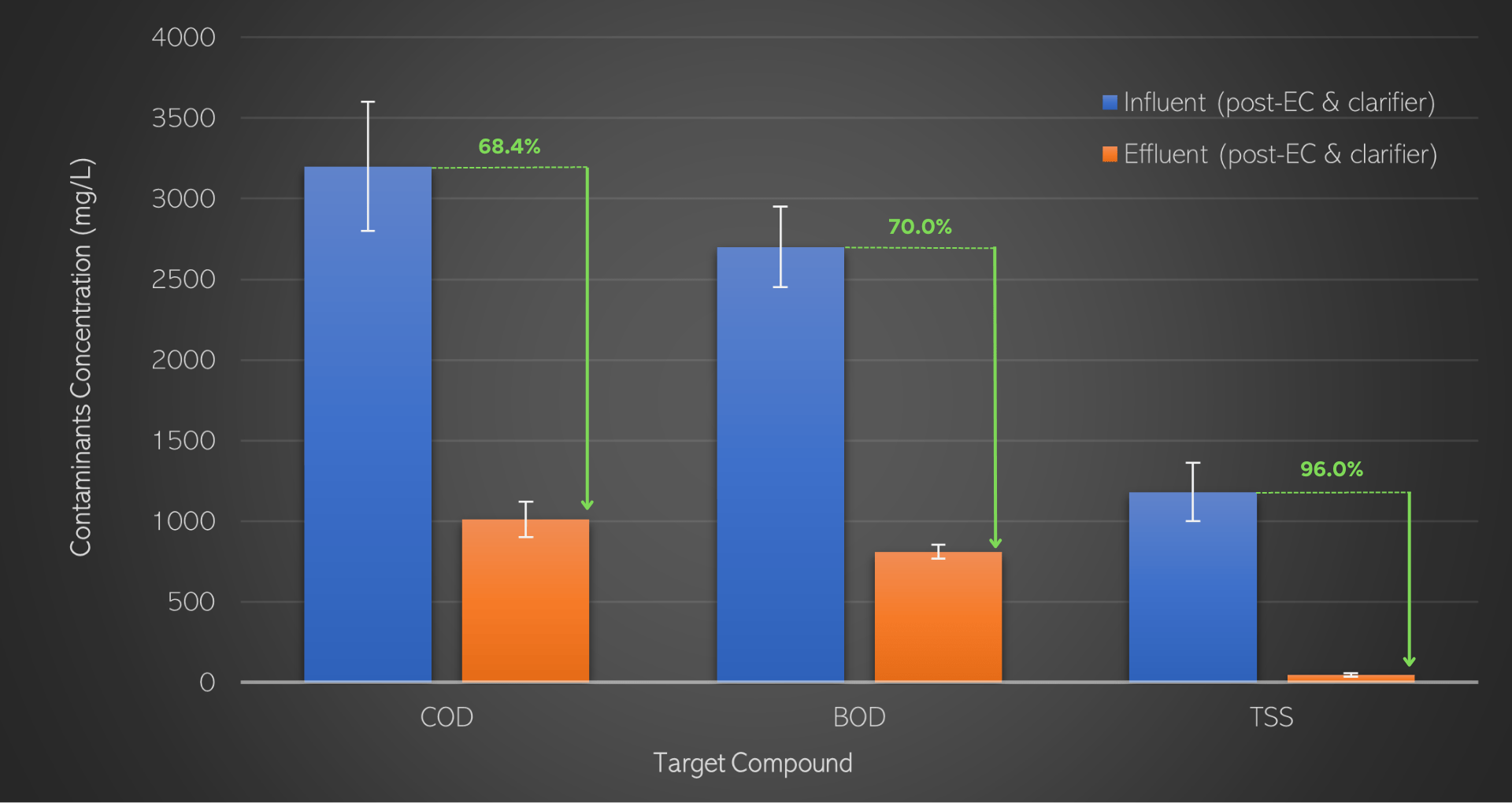

Overall, the Hydroleap system is a highly effective wastewater treatment solution that can help food and beverage companies meet environmental regulations and protect water resources.


