Introduction to Electrocoagulation
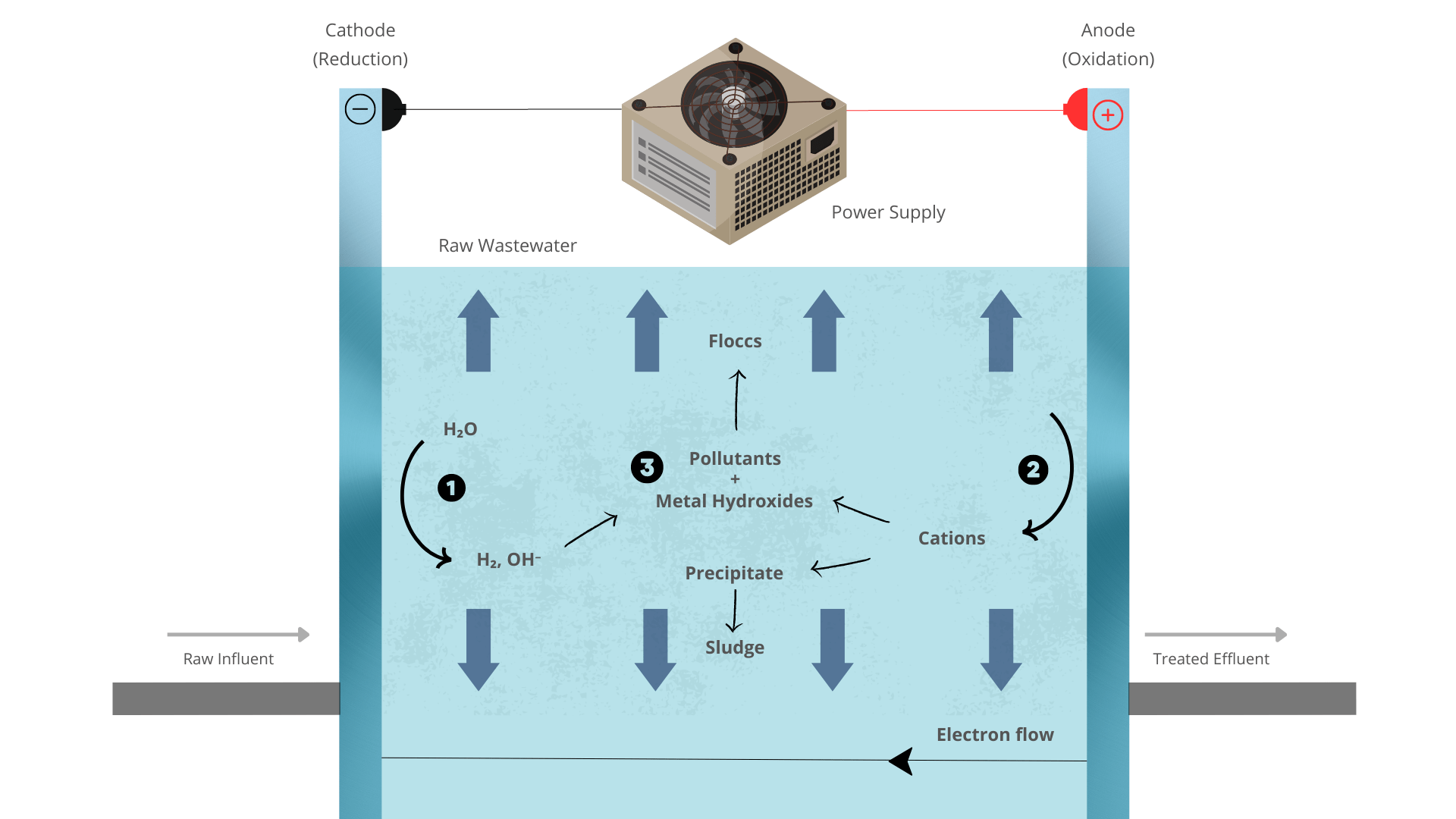
Electrocoagulation is an electrochemical process that utilizes the principle of electrolysis to remove contaminants from water and wastewater. It is a promising and sustainable technology that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its effectiveness in treating various types of industrial effluents and municipal wastewater. Electrocoagulation involves the application of a low-voltage electrical current to the contaminated water, leading to the coagulation and precipitation of suspended particles, colloids, and dissolved substances. This process offers several advantages over conventional coagulation methods and has found applications in a wide range of industries.
Main Mechanisms of Electrocoagulation
The electrocoagulation process involves the use of sacrificial electrodes, typically made of aluminium or iron, which are connected to a power supply. When the electrodes are energized, they undergo electrochemical reactions. In the case of aluminium electrodes, aluminium ions are generated at the anode, while hydroxyl ions are produced at the cathode. These aluminium ions and hydroxyl ions play a crucial role in the coagulation process.
The aluminium ions neutralize the negatively charged particles and colloids present in the water through charge neutralization. They form aluminium hydroxide complexes, which act as coagulants and destabilize the particles. The hydroxyl ions generated at the cathode raise the pH near the cathode, promoting the precipitation of metal hydroxides. The coagulated particles and precipitates can then be removed through sedimentation or filtration processes.
Applications of Electrocoagulation
- Removal of heavy metals: Electrocoagulation can efficiently remove heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, copper, and chromium from industrial wastewater generated by metal plating, mining, and metal finishing operations.
- Organic pollutant removal: It is effective in treating organic pollutants like dyes, phenols, oils, and hydrocarbons. Industries such as textile, petrochemical, and food processing can benefit from electrocoagulation for the removal of organic contaminants.
- Suspended solids removal: Electrocoagulation can effectively coagulate and remove suspended solids, turbidity, and particulate matter from wastewater, enhancing its clarity and reducing its environmental impact.
- Phosphate removal: Electrocoagulation has been successfully employed for phosphate removal in wastewater treatment, particularly in the agricultural sector where excess phosphates from fertilizers can lead to water pollution and eutrophication.
Advantages of Electrocoagulation
- Versatility: Electrocoagulation is applicable to a wide range of contaminants, making it a versatile treatment option for various industries and wastewater types.
- Effectiveness: Electrocoagulation has demonstrated high removal efficiencies for various pollutants, including heavy metals, suspended solids, and organic compounds.
- Lower chemical consumption: Unlike traditional coagulation processes, electrocoagulation requires minimal or no addition of chemical coagulants, reducing the chemical costs and the associated chemical handling and storage issues.
- Sludge minimization: The process generates voluminous metal hydroxide sludge, which can be easily separated from the treated water. The sludge may be further treated for metal recovery or disposed of safely.
How Hydroleap Optimizes Performance
- Energy efficiency: Electrocoagulation systems have been optimized for energy consumption, ensuring efficient operation while treating water of varying qualities. Our advanced technology minimizes energy requirements, resulting in cost savings for our customers.
- Long-term cost-effectiveness: Although initial installation and maintenance costs may be higher for larger-scale applications, our electrocoagulation systems are designed to provide long-term cost-effectiveness. The durability and reliability of our equipment ensure reduced maintenance needs, resulting in overall savings over time.
- Enhanced process flexibility: Our electrocoagulation systems are designed to accommodate a wide range of wastewater conditions. While initial pH adjustment may be required for optimal process efficiency, this feature allows us to tailor the treatment process to suit different applications, ensuring effective and customized solutions.
- Scalability with innovation: While scaling up electrocoagulation for large-scale applications presents challenges, our team of experts has developed innovative solutions to overcome these obstacles. Our cutting-edge electrode design and anti-fouling technology ensure efficient and scalable operations, making electrocoagulation a viable option for various industries and water treatment needs.
Conclusion
Electrocoagulation is a promising water treatment technology with the potential to address a wide range of contaminants found in industrial and municipal wastewater. It offers numerous advantages such as versatility, high removal efficiency, and reduced chemical consumption. However, it is important to consider the associated energy consumption, equipment costs, and pH adjustment requirements. With further research and development, electrocoagulation has the potential to become a more widely adopted solution for sustainable water and wastewater treatment.


